Asynchronous services
(go to async page) (go to day 2)
Asynchronous services, first day (Feb 11th)
(NB jmfernandez: although I remember the faces, I do not remember some names of the participants in the initial discussion. Sorry! In those cases I have used three questions '???' as placeholders).
Initial topics, in their original order, were:
- Is it worth WSRF?
- Is it worth for short (aka fast), easy services, to become an asynchronous service?
- Is it easy from the service developer's point of view to create/develop the needed infrastructure for an asynchronous web service?
- Is it easy from the client developer's point of view to deal with an asynchronous web service?
We were taking into account the different web services paradigms used in bioinformatics, and also projects and major service providers we knew with some asynchronous capability. So, the additional topic was introduced by Matthew Pocock:
- How are asynchronous services being implemented in our projects just now?
We agreed that main web services paradigms used in bioinformatics are REST, SOAP+ WSDL, SoapLab 1 & SoapLab 2, and BioMOBY. Meanwhile we were discussing we identified some major service providers which have implemented or want to implement asynchronous services: DDBJ WABI, PDBj, EBI-EMBOSS (which uses SoapLab?), EMBRACE NoE and InstantSOAP. We were quite sure that NCBI provides such services, but we did not have any attending people who came from NCBI which could confirm it. INB has also some BioMOBY asynchronous services, but they were not mentioned in that moment.
Then, we were talking about WSRF implementation in BioMOBY, WSRF support in the different languages used in bioinformatics, and in general asynchronous models. José María Fernández explained that WSRF::Lite (the Perl WSRF library) is being maintained, and its maintainers are quite responsive to suggestions and changes. He also told that he was looking six months ago for a Java library implementing last WSRF specifications, but he only found the old, outdated ones, from Globus Toolkit. Just ??? pointed out that Apache Foundation has Apache Muse a project about implementing WSRF in Java, which was developed taking into account last WSRF specifications.
At last, these topics drove us to the next one (pointed by Matthew):
- Which asynchronous model is better, a polling mechanism or a callback model?
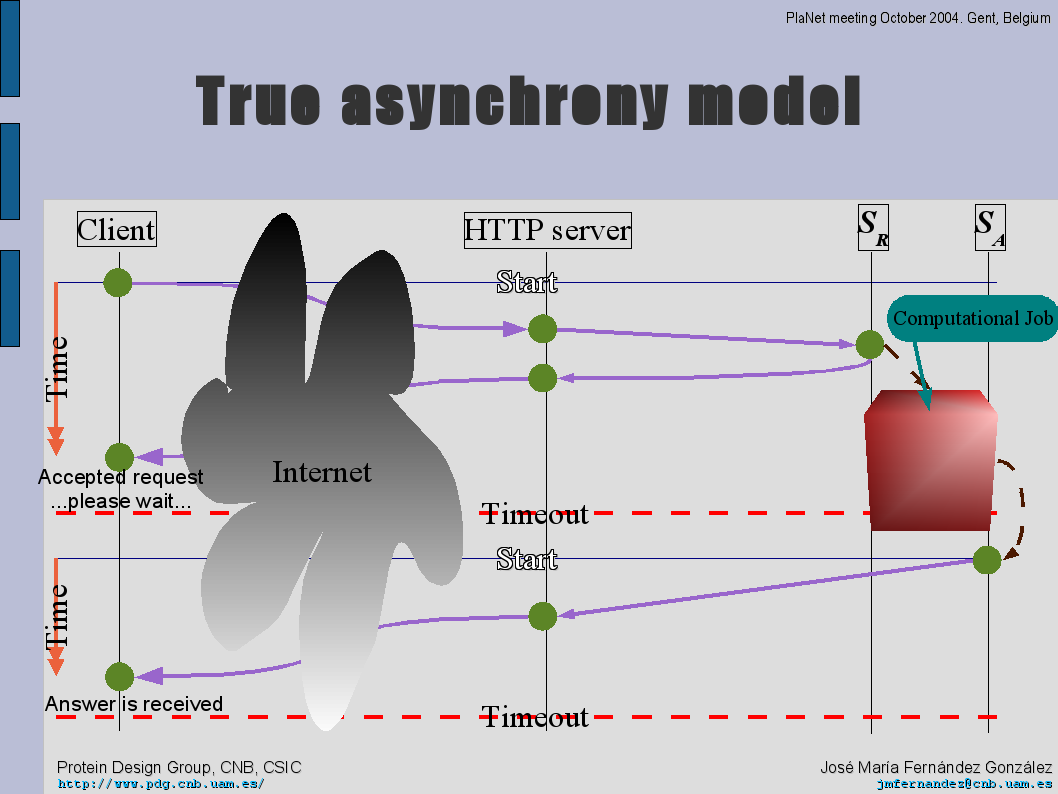
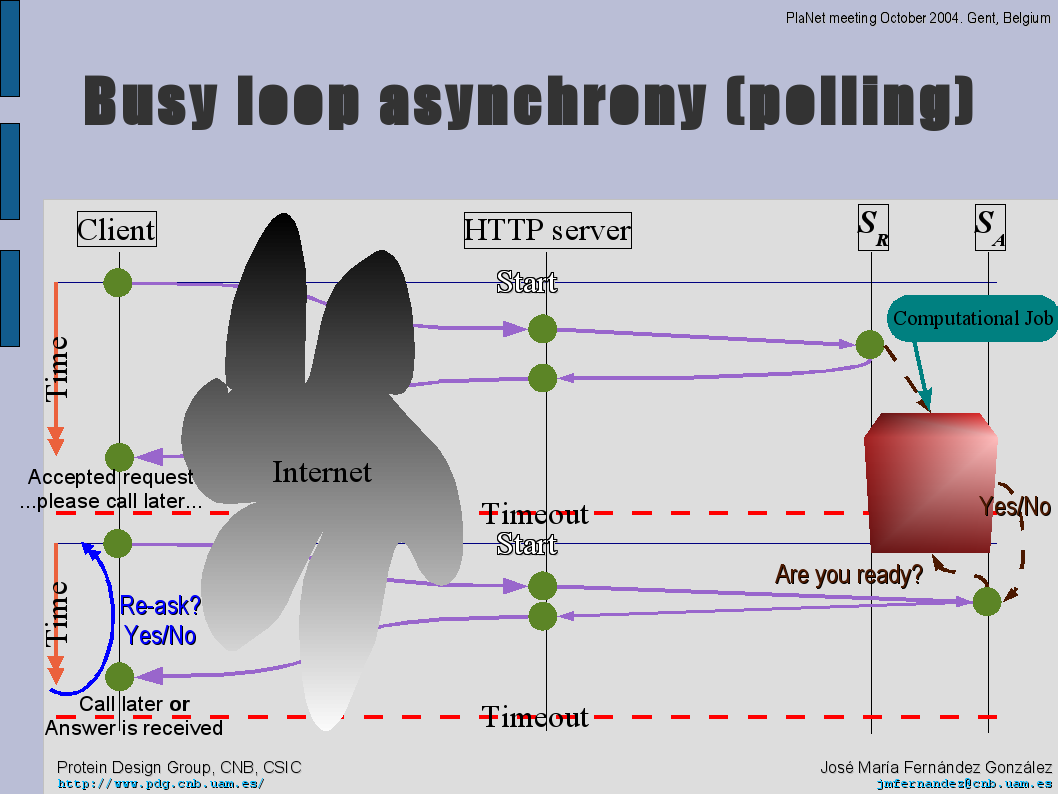
José María Fernández showed some slides about asynchronous model and HTTP:
- The roles inside asynchronous models applied to HTTP.
- The flow of a true asynchronous, callback model, where the asynchronous client can be actively notified by the service when this last one has finished.
- And a polling mechanism, where the asynchronous client sends status update queries to the server, until the result is prepared or the service has failed.
??? asked if it would be worth the model followed by some AJAX applications using asynchronous services to be able to have an active service notification. Although it was not identified then, this model is Comet. The information has been provided by José Manuel Rodríguez (INB) by e-mail, and he suggested us also to read Why Comet? and Ajax, a new approach to web applications.
This model maintains an open socket sending echo messages to avoid HTTP timeouts, but it was discarded because it was not reliable (once the connection is lost, the client should reconnect to the service, sending the job identifier. Then ??? told us about a way to send/set job identifier as an HTTP header, so it is an out-of-band parameter (it does not need to be set as an explicit call parameter to the web service).
In this point, ??? complained about problems like service overloading when polling mechanism is in usage: a client hits too fast the asynchronous service. José María Fernández told that the service could/should optionally provide the polling frequency it likes just when the job identifier is returned.
We came back to WSRF and BioMOBY. Some of the participants asked about the implementation, its stability in the protocol for future versions, why there is no support for Asynchronous MOBY in Taverna and if there is any service already implemented and working. José María Fernández could explain its experience in this field, because he polished (with the help of José Manuel Rodríguez, INB) the implementation of Asynchronous MOBY previously done by INB. Also, ??? asked about how difficult could be implementing WSRF in Ruby, and ??? complained about BioMOBY services. This last complain was focused on the fact that BioMOBY uses WSRF, which is a WS-I standard, but it does not follow other standards like WS Management or WS Addressing. Also, some attenders complained about the fact that BioMOBY does not define an XML Schema for their messages and that any MOBY message itself is packaged as an string, many times encoded with Base64. Eddie Kawas incorporated to the discussion, explaining some of these points to the attenders. Matthew Pocock pointed out that it is easier to develop a client program using SOAP when the XML schema of the messages is available, because messages can be validated and also some toolkits can auto-generate glue code to ease the development steps both in client and service sides.
We started also talking about throwing away WSRF from our discussion, due it is not so widespread as it was expected a couple of years ago, and replacing it with a custom solution.